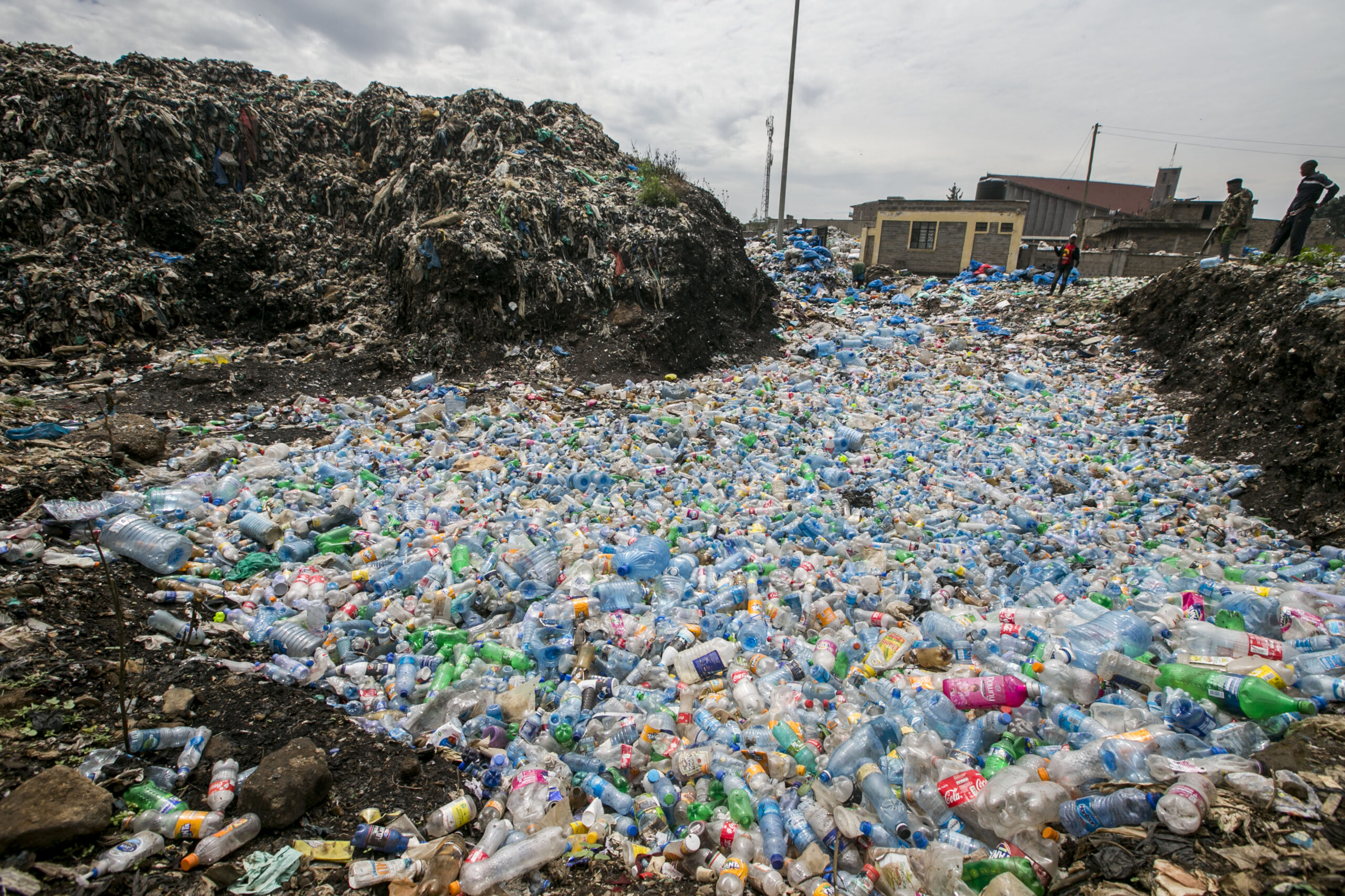

With an estimated population of
about 201 million people in 2019 by the United Nations, Nigeria is projected to be one of the highest generators of plastic waste in Africa. Waste generation is an integral part of human activity influenced by social dynamics and economic development. An increase in per capita income, consumption, urbanization, and population in the last two decades, combined with a lack of sufficient waste management infrastructure has led to an increase in waste generation and environmental pollution, posing one of the most pressing environmental challenges in the country.
Nigeria generates an estimated 32 million tonnes of solid waste yearly, one of the highest in Africa, from that figure, plastic constitutes 2.5 million tonnes. Nigeria is among the top 20 nations that contribute 83 percent of the total volume of land-based plastic waste that ends up in the oceans. An estimate of over 200,000 metric tonnes of plastic waste from land-based sources in Nigeria is discharged into the Atlantic Ocean annually.
Plastics pollution, particularly single-use plastic is visible in major cities in Nigeria due to the ineffectiveness of waste management systems. Marine pollution causes environmental, economic, health, and aesthetic problems. The solution to these endemic problems includes reduction, reuse, increased recycling, tough litter abatement laws, and well-run municipal waste management systems.
Given the inadequate public infrastructure to supply drinking water, the private sector started producing plastic or nylon-packed sachet water, popularly known as 'pure water'. Sachet water has since diffused among the population as a source of potable drinking water, with 70 percent of Nigerians individually consuming an average of one bag of sachet water daily during the dry season, according to a
Study On Plastics Value Chain In Nigeria 2021 Report.
Given the ubiquitous nature of plastics as part of our everyday lives, plastic has brought numerous benefits in enabling several cutting-edge technologies and significantly reducing food waste. Little wonder plastic remains a valuable material that needs to be used responsibly and managed by everyone in an environmentally safe manner at the end of its life.
Plastic use and production are often portrayed in highly negative terms in the media as the public reconcile with the realities of mismanaged plastic waste. However, making smart choices about plastic consumption and educating ourselves about how to value this material experts believe is the best way forward.
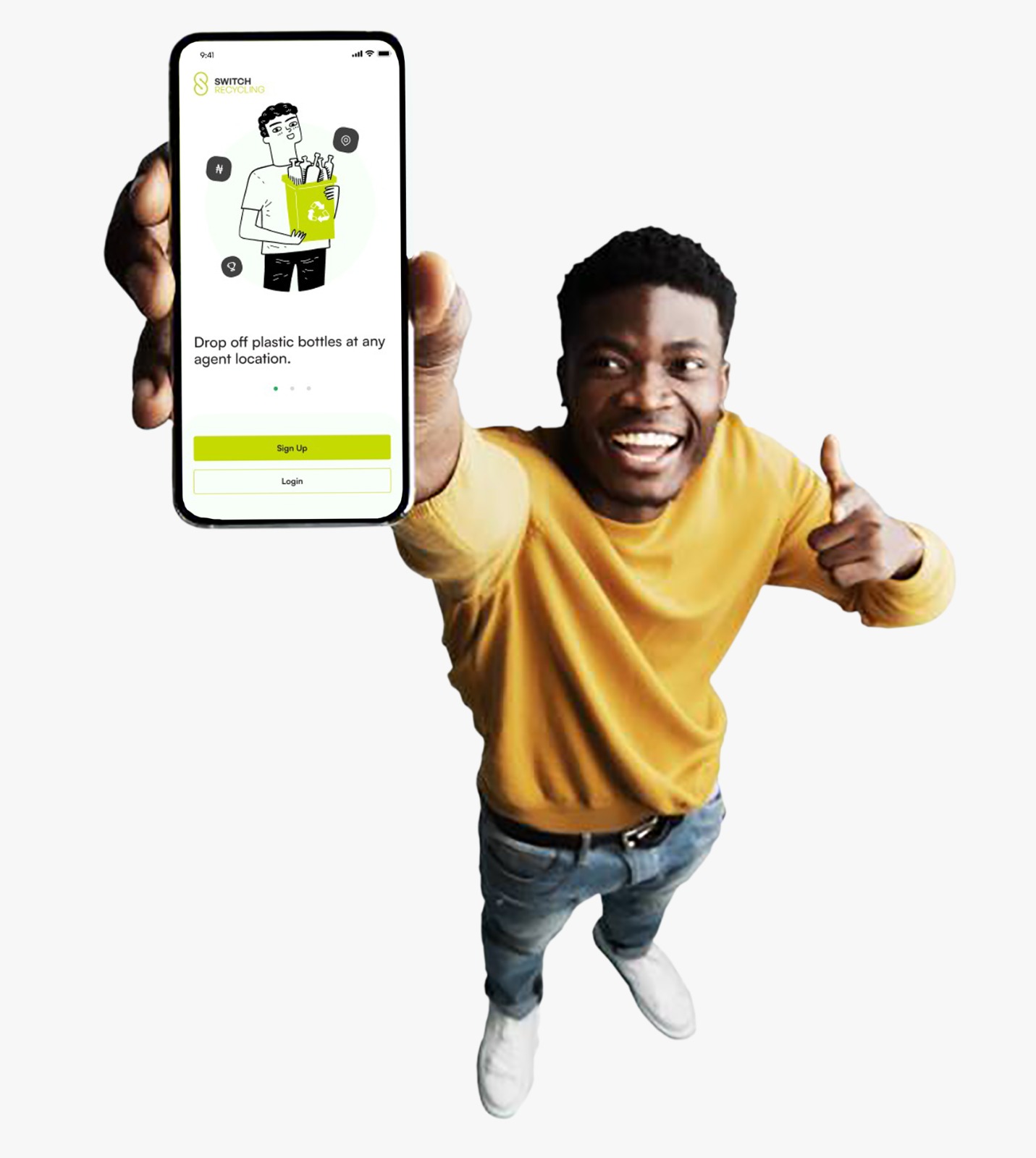
What ‘Switch Recycling’ is doing?
In actualizing its vision of building the most efficient platform for wealth creation via post-consumer waste recovery across Africa, Switch Recycling Innovations has developed a mobile application solution that enables people to dispose of plastic waste from the comfort of their homes without any stress.
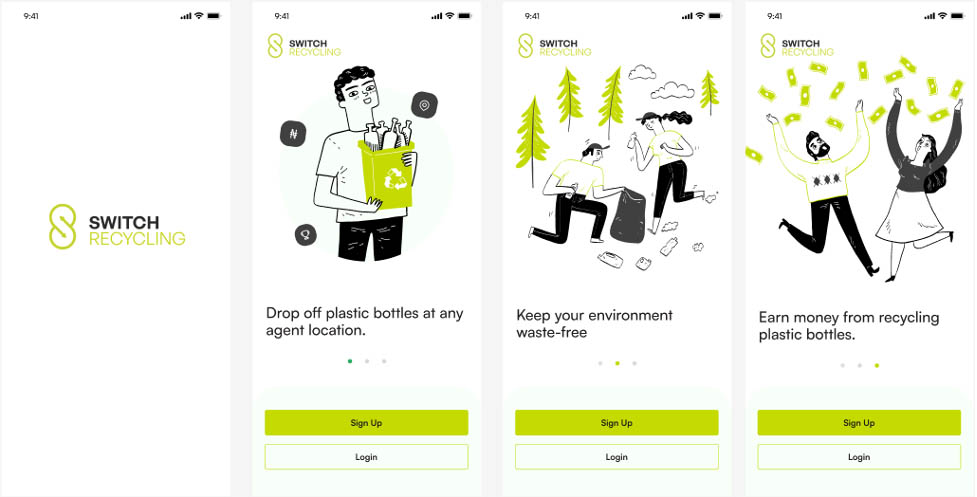
The mobile application is designed to drive positive attitudinal change towards waste disposal by allowing users to dispose their plastic waste and receive instant payment through the integration of financial technology services thereby playing a role in the circular economy ecosystem. This is to encourage an eco-friendlier environment while getting rewarded for properly disposing of waste material. The application is designed to cater to both individual households and Agents.
Switch Recycling adopted the approved National Policy on Plastic Waste Management in developing a cutting-edge tech app that will drive plastic collection from households, and institutions across Nigeria and West Africa at large. This is expected to cause a positive attitudinal change in the way plastic wastes are managed and disposed of. In the long run, this will be instrumental in limiting the littering of single-use plastic packaging products and waste materials in major cities across the country.
The Switch Recycling Innovation philosophy is ‘promoting an eco-friendly environment via tech, improving financial inclusion, and contributing to social responsibility frameworks through PET contributions to charities.’ This is in line with the 2015 National Environmental Sanitation Policy that seeks to promote appropriate technologies for recycling waste components like plastics.
Addressing post-consumption challenges
Driving post-consumption collection and recycling of PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) and LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene) plastics is not only environmentally responsible but also a potential business opportunity. Post-consumption challenges can be addressed through the following:
Education and Awareness
1. Launching educational campaigns to inform the public about the importance of recycling PET and LDPE plastics.
2. Partnering with educational institutions, community organizations, and local governments to promote plastic recycling.

Responsible Consumption and Production
Driving responsible consumption and production by collecting, and processing PET and LDPE bottles. This process will minimize waste.
Regulatory Compliance
Staying updated with environmental regulations and ensuring compliance in waste handling and recycling processes.
Research and Development
Investing in Research and Development (R and D) to explore innovative recycling technologies that improve the efficiency of plastic waste collection and recycling.
Partnerships and Collaborations
Collaborating with organizations, NGOs, and other stakeholders working toward plastic waste collection and a cleaner environment.
Driving post-consumption collection and recycling of PET and LDPE plastics is pivotal in achieving a cleaner and healthier society. By combining effective waste collection, cutting-edge recycling technology, and sustainable business practices, organisations can play a crucial role in reducing plastic pollution and contributing to a circular economy.
 With an estimated population of about 201 million people in 2019 by the United Nations, Nigeria is projected to be one of the highest generators of plastic waste in Africa. Waste generation is an integral part of human activity influenced by social dynamics and economic development. An increase in per capita income, consumption, urbanization, and population in the last two decades, combined with a lack of sufficient waste management infrastructure has led to an increase in waste generation and environmental pollution, posing one of the most pressing environmental challenges in the country.
Nigeria generates an estimated 32 million tonnes of solid waste yearly, one of the highest in Africa, from that figure, plastic constitutes 2.5 million tonnes. Nigeria is among the top 20 nations that contribute 83 percent of the total volume of land-based plastic waste that ends up in the oceans. An estimate of over 200,000 metric tonnes of plastic waste from land-based sources in Nigeria is discharged into the Atlantic Ocean annually.
Plastics pollution, particularly single-use plastic is visible in major cities in Nigeria due to the ineffectiveness of waste management systems. Marine pollution causes environmental, economic, health, and aesthetic problems. The solution to these endemic problems includes reduction, reuse, increased recycling, tough litter abatement laws, and well-run municipal waste management systems.
Given the inadequate public infrastructure to supply drinking water, the private sector started producing plastic or nylon-packed sachet water, popularly known as 'pure water'. Sachet water has since diffused among the population as a source of potable drinking water, with 70 percent of Nigerians individually consuming an average of one bag of sachet water daily during the dry season, according to a Study On Plastics Value Chain In Nigeria 2021 Report.
Given the ubiquitous nature of plastics as part of our everyday lives, plastic has brought numerous benefits in enabling several cutting-edge technologies and significantly reducing food waste. Little wonder plastic remains a valuable material that needs to be used responsibly and managed by everyone in an environmentally safe manner at the end of its life.
Plastic use and production are often portrayed in highly negative terms in the media as the public reconcile with the realities of mismanaged plastic waste. However, making smart choices about plastic consumption and educating ourselves about how to value this material experts believe is the best way forward.
With an estimated population of about 201 million people in 2019 by the United Nations, Nigeria is projected to be one of the highest generators of plastic waste in Africa. Waste generation is an integral part of human activity influenced by social dynamics and economic development. An increase in per capita income, consumption, urbanization, and population in the last two decades, combined with a lack of sufficient waste management infrastructure has led to an increase in waste generation and environmental pollution, posing one of the most pressing environmental challenges in the country.
Nigeria generates an estimated 32 million tonnes of solid waste yearly, one of the highest in Africa, from that figure, plastic constitutes 2.5 million tonnes. Nigeria is among the top 20 nations that contribute 83 percent of the total volume of land-based plastic waste that ends up in the oceans. An estimate of over 200,000 metric tonnes of plastic waste from land-based sources in Nigeria is discharged into the Atlantic Ocean annually.
Plastics pollution, particularly single-use plastic is visible in major cities in Nigeria due to the ineffectiveness of waste management systems. Marine pollution causes environmental, economic, health, and aesthetic problems. The solution to these endemic problems includes reduction, reuse, increased recycling, tough litter abatement laws, and well-run municipal waste management systems.
Given the inadequate public infrastructure to supply drinking water, the private sector started producing plastic or nylon-packed sachet water, popularly known as 'pure water'. Sachet water has since diffused among the population as a source of potable drinking water, with 70 percent of Nigerians individually consuming an average of one bag of sachet water daily during the dry season, according to a Study On Plastics Value Chain In Nigeria 2021 Report.
Given the ubiquitous nature of plastics as part of our everyday lives, plastic has brought numerous benefits in enabling several cutting-edge technologies and significantly reducing food waste. Little wonder plastic remains a valuable material that needs to be used responsibly and managed by everyone in an environmentally safe manner at the end of its life.
Plastic use and production are often portrayed in highly negative terms in the media as the public reconcile with the realities of mismanaged plastic waste. However, making smart choices about plastic consumption and educating ourselves about how to value this material experts believe is the best way forward.

 The mobile application is designed to drive positive attitudinal change towards waste disposal by allowing users to dispose their plastic waste and receive instant payment through the integration of financial technology services thereby playing a role in the circular economy ecosystem. This is to encourage an eco-friendlier environment while getting rewarded for properly disposing of waste material. The application is designed to cater to both individual households and Agents.
Switch Recycling adopted the approved National Policy on Plastic Waste Management in developing a cutting-edge tech app that will drive plastic collection from households, and institutions across Nigeria and West Africa at large. This is expected to cause a positive attitudinal change in the way plastic wastes are managed and disposed of. In the long run, this will be instrumental in limiting the littering of single-use plastic packaging products and waste materials in major cities across the country.
The Switch Recycling Innovation philosophy is ‘promoting an eco-friendly environment via tech, improving financial inclusion, and contributing to social responsibility frameworks through PET contributions to charities.’ This is in line with the 2015 National Environmental Sanitation Policy that seeks to promote appropriate technologies for recycling waste components like plastics.
The mobile application is designed to drive positive attitudinal change towards waste disposal by allowing users to dispose their plastic waste and receive instant payment through the integration of financial technology services thereby playing a role in the circular economy ecosystem. This is to encourage an eco-friendlier environment while getting rewarded for properly disposing of waste material. The application is designed to cater to both individual households and Agents.
Switch Recycling adopted the approved National Policy on Plastic Waste Management in developing a cutting-edge tech app that will drive plastic collection from households, and institutions across Nigeria and West Africa at large. This is expected to cause a positive attitudinal change in the way plastic wastes are managed and disposed of. In the long run, this will be instrumental in limiting the littering of single-use plastic packaging products and waste materials in major cities across the country.
The Switch Recycling Innovation philosophy is ‘promoting an eco-friendly environment via tech, improving financial inclusion, and contributing to social responsibility frameworks through PET contributions to charities.’ This is in line with the 2015 National Environmental Sanitation Policy that seeks to promote appropriate technologies for recycling waste components like plastics.

